Damper Force Equation . When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot damper differential equation is of a special type; — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. — forced vibrations with damping. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is:
from www.chegg.com
the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. — forced vibrations with damping. — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. damper differential equation is of a special type; \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot
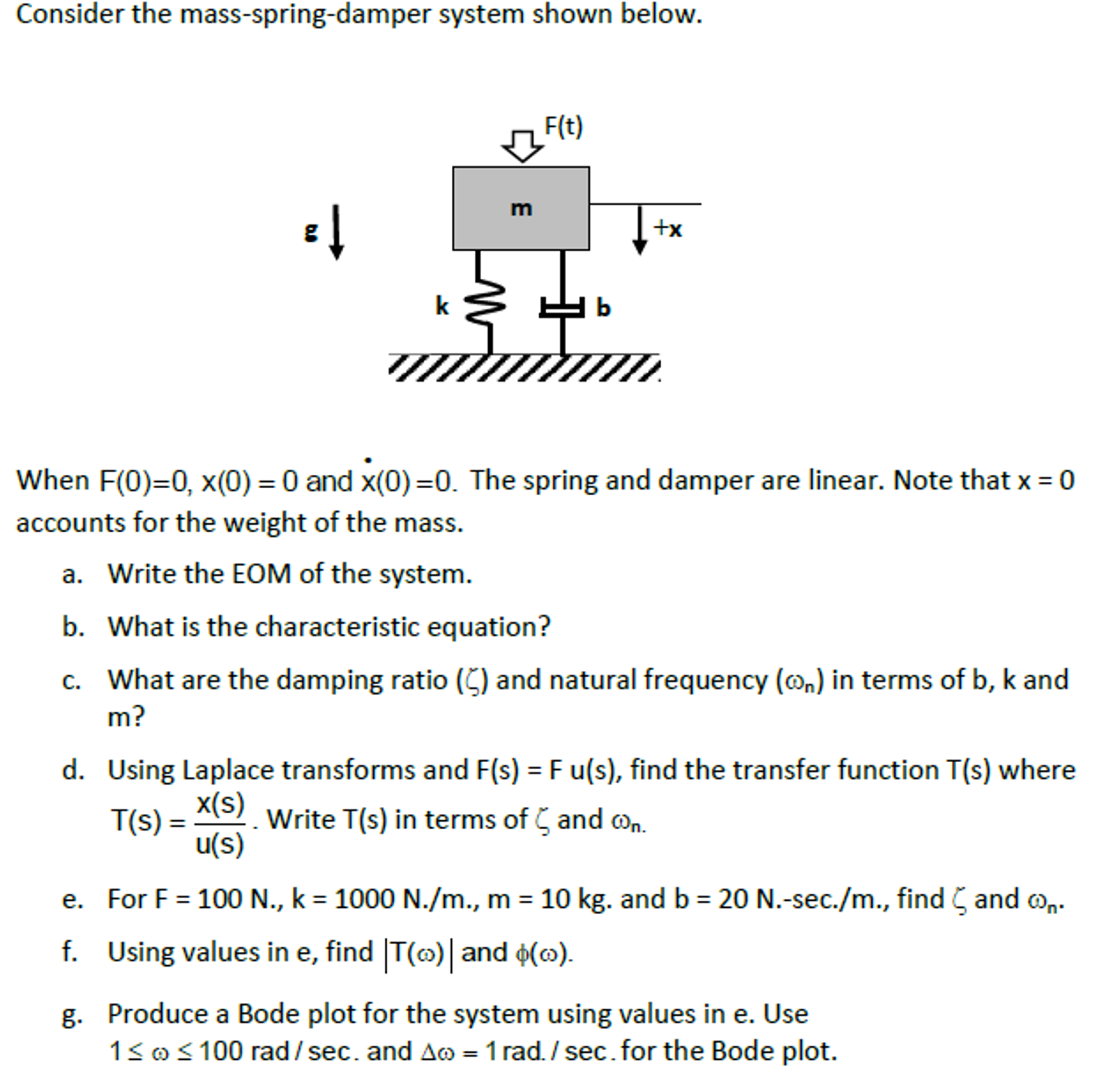
Solved Consider the massspringdamper system shown below.
Damper Force Equation the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. — forced vibrations with damping. damper differential equation is of a special type;
From www.transtutors.com
(Solved) The Mass, Spring, And Damper System Shown Below Is At Rest Damper Force Equation — forced vibrations with damping. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. damper differential equation is of a special type; \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot When the extension. Damper Force Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Q10.* (10 marks) Figure 1 below depicts the popular Damper Force Equation When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. damper differential equation is of a special type; The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force. Damper Force Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Consider the MassSpringDamper System shown in Damper Force Equation When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system.. Damper Force Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The force equation of the mass spring damper system Damper Force Equation damper differential equation is of a special type; — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity.. Damper Force Equation.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Task 5 Laplace Transform and Differential Equations (20 marks Damper Force Equation — forced vibrations with damping. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. damper differential equation is of a special. Damper Force Equation.
From adaptivemap.ma.psu.edu
Mechanics Map Viscous Damped Free Vibrations Damper Force Equation — forced vibrations with damping. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. . Damper Force Equation.
From www.researchgate.net
(a) Springdamper equation and (b) electrostatic force blocks Damper Force Equation the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. — forced vibrations with damping.. Damper Force Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Damped Oscillations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Damper Force Equation The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: damper differential equation is of a special type; \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot — forced vibrations with damping. — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. — the. Damper Force Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Massspringdamper Tutorial YouTube Damper Force Equation damper differential equation is of a special type; When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. The equation for the force or moment produced. Damper Force Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved A springmassdamper system is shown below; the Damper Force Equation — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. damper differential equation is of a special type; — forced vibrations with damping. \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. The equation for the force or. Damper Force Equation.
From www.scribd.com
Mass Spring Damper Equations Mathematical Analysis Damper Force Equation damper differential equation is of a special type; — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. \[ \vec{f}_c. Damper Force Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved MATLAB Program Problem A classical mechanical Damper Force Equation — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. — forced vibrations with damping. \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot. Damper Force Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Lecture 4 EQUATION OF MOTION FOR VISCOUS DAMPING Part 2 [ Structural Damper Force Equation — forced vibrations with damping. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards. Damper Force Equation.
From www.youtube.com
How to design two Mass Damper Spring System in Simulink? YouTube Damper Force Equation The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. — forced vibrations with damping. — we will only consider linear viscous. Damper Force Equation.
From mail.sharetechnote.com
Differential Equation Modeling Spring and Mass ShareTechnote Damper Force Equation the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system.. Damper Force Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Mass Spring Dampers Equation of Motion Dampened Harmonic Motion Damper Force Equation — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping force is linearly proportional to velocity. — forced vibrations with damping. The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system.. Damper Force Equation.
From study.com
Damping Ratio & Coefficient Formula, Units & Examples Video Damper Force Equation the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that motion, hence the damper force f d = − c d y d t,. — the damping equation provides a mathematical representation of the damping force acting on a system. — we will only consider linear viscous dampers, that is where the damping. Damper Force Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The equation of motion of a springmassdamper system Damper Force Equation damper differential equation is of a special type; The equation for the force or moment produced by the damper, in either \(x\) or \(\theta\), is: \[ \vec{f}_c = c \vec{\dot When the extension $x$ is positive (assumed downwards from the diagram) the spring is. the damper resists any motion with a force proportional to the velocity of that. Damper Force Equation.